(Source: ENR.com & Wall Street Journal)
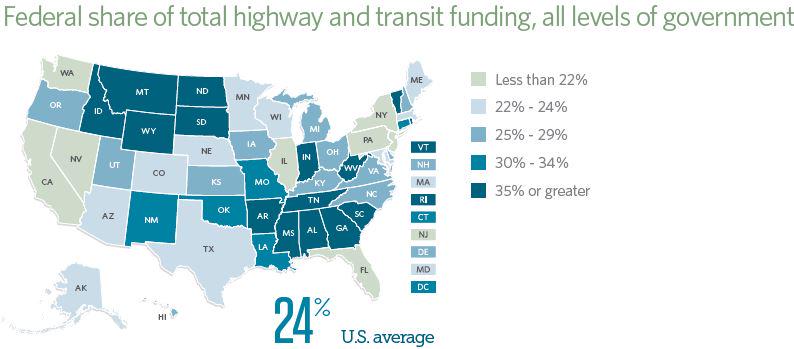
The Obama administration said as much as $17 billion in additional federal money is needed to maintain roads and bridges over the next two years, underscoring the challenges policy makers face as driving habits change.

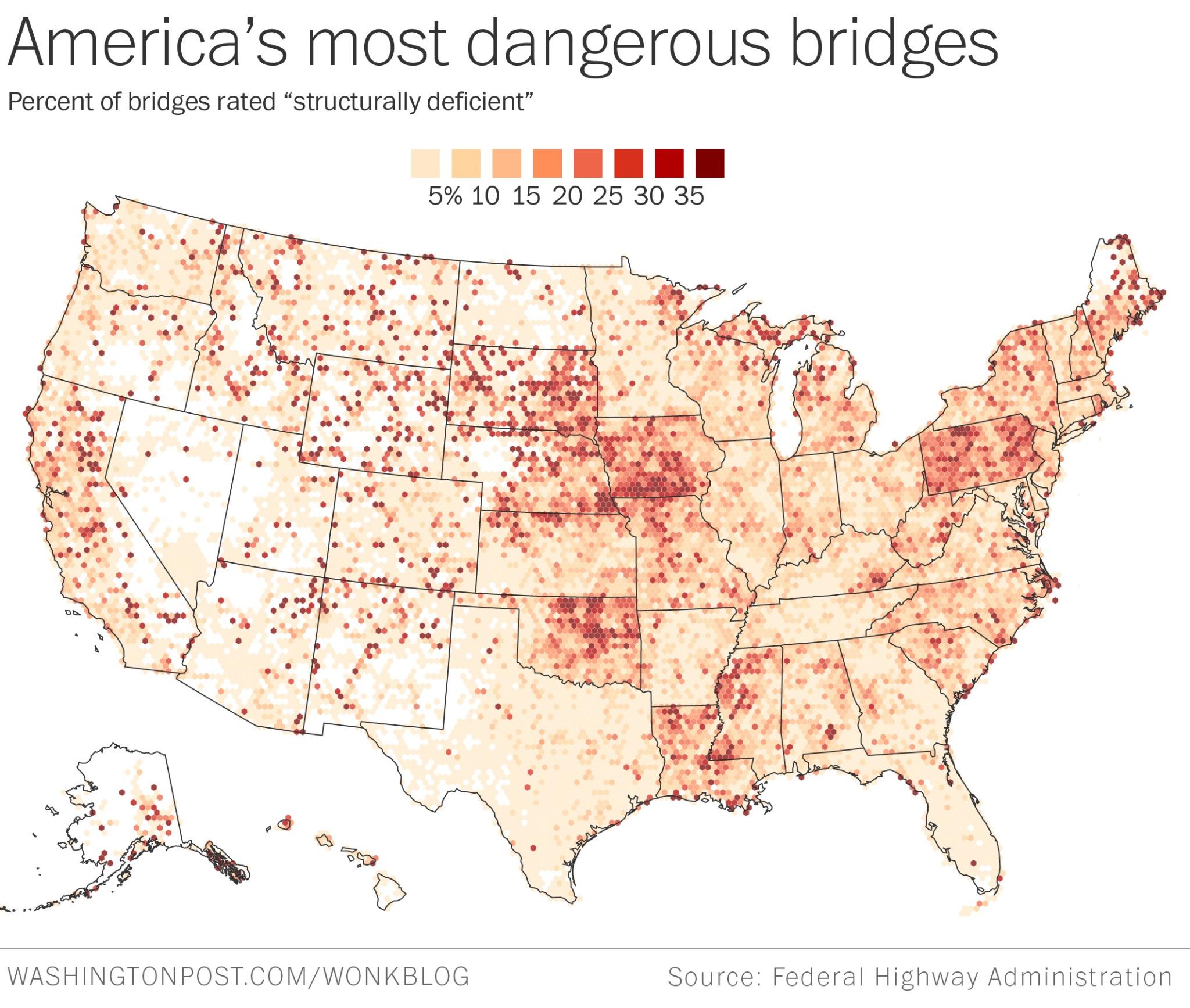
Image Courtesy; Stateline.org via Gmanet.com
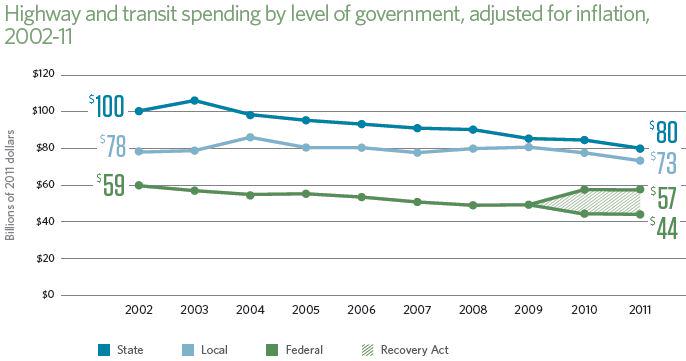
The recession and gas-price increases over the past two years have caused many consumers to drive less and switch to more fuel-efficient cars. The result has been a fall in revenue from taxes on gasoline and vehicle purchases, which are used to fund state and local transportation projects.
Officials from the Obama administration and U.S. Dept. of Transportation have said that the trust fund will not have enough cash to cover commitments to states for highway projects, according to Senate Environment and Public Works Committee Chairman Barbara Boxer (D-Calif.) and the panel’s top Republican, James Inhofe of Oklahoma.
According to administration and DOT officials, $5 billion to $7 billion will be needed by August to avert having to slow down Federal Highway Administration reimbursements to state DOTs, Boxer and Inhofe said on June 2. The lawmakers added that a further $8 billion to to $10 billion will be needed in fiscal year 2010 to maintain the highway program at its current level. Congress has set the 2009 federal highway program obligation limit at $40.7 billion.
Boxer and Inhofe discussed the trust fund’s problem at a June 2 committee hearing on the nomination of former Arizona DOT Director Victor Mendez to be the new head of the Federal Highway Administration.
Inhofe raised the possibility of tapping the interest on the Highway Trust Fund balance as one solution. That interest goes to the general Treasury, not the trust fund.
The administration has resisted calls to increase the 18.4-cent federal tax on a gallon of gas; the tax hasn’t been raised since 1993.
Last year, Congress transferred $8 billion from the government’s general fund to the highway trust fund in response to a similar shortfall, allowing states to move ahead with hundreds of job-creating transportation projects. Congress may do that again this year.
Lawmakers could also consider tweaking the economic-stimulus law so states could use some of their stimulus money to compensate for other budget shortfalls. In most cases, states can’t use stimulus funds to compensate for budget deficits in their transportation-spending plans.
Congress and the administration are crafting legislation that would determine how the federal government funds transportation projects over the next several years. With the White House opposed to a gas-tax increase, lawmakers are trying to identify new money sources to maintain the nation’s infrastructure.
One hint of their approach could come later this month when Rep. James Oberstar (D., Minn.), chairman of the House Transportation and Infrastructure Committee, is slated to unveil his blueprint for transportation spending.