Food vs. Fuel – As the world diverts more food crops to making fuel, citizens around the globe feel the pressure
(Source: NY Times)
U.S. Doctors Say Biofuels Could Kill Over 192,000 Per Year in Developing Countries
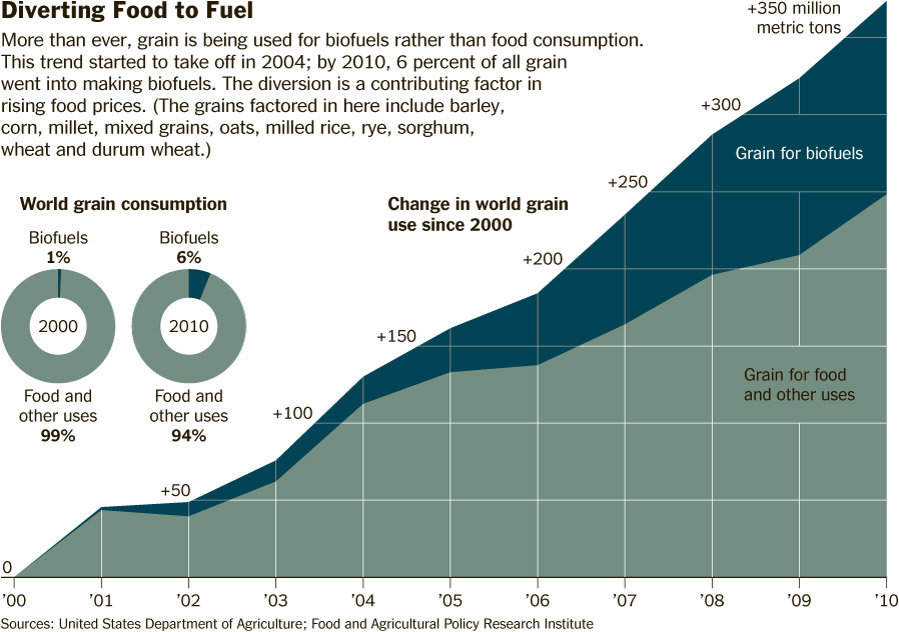
The food vs. fuel debate has intensified a little more with the ever growing demand for bio-fuels. Many of the world’s hungriest people are going to bed without a morsel to eat, as more of the conventional food crops such as corn are diverted towards making biofuels that power the vehicle fleets. This above graphic from the NY Times article shows an alarming increase in the way we have change the consumption from food to fuel starting at the dawn of this 21st century.
Each year, an ever larger portion of the world’s crops — cassava and corn, sugar and palm oil — is being diverted for biofuels as developed countries pass laws mandating greater use of nonfossil fuels and as emerging powerhouses like China seek new sources of energy to keep their cars and industries running. Cassava is a relatively new entrant in the biofuel stream.
But with food prices rising sharply in recent months, many experts are calling on countries to scale back their headlong rush into green fuel development, arguing that the combination of ambitious biofuel targets and mediocre harvests of some crucial crops is contributing to high prices, hunger and political instability.
This year, the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization reported that its index of food prices was the highest in its more than 20 years of existence. Prices rose 15 percent from October to January alone, potentially “throwing an additional 44 million people in low- and middle-income countries into poverty,” the World Bank said.
On a related note, the following was published on TreeHugger.com:
The Association of American Physicians and Surgeons (AAPS) has released a warning that U.S. and European policy to increase the production of biofuels could lead to almost 200,000 deaths in poorer countries. How? Mostly through higher food prices. Most biofuels are made using food crops like corn at this time, and diverting corn to ethanol refineries not only increases the price of corn, but it also encourage farmers to plant more of it, leaving less space for other types of crops, driving up their price too. This is a big deal if you live on $1-2 a day…