(Source: Fortune Magazine via CNN Money)

Images via Apture
When lunch break comes at the construction site between Shanghai and Suzhou in eastern China, Xi Tong-li and his fellow laborers bolt for some nearby trees and the merciful slivers of shade they provide.
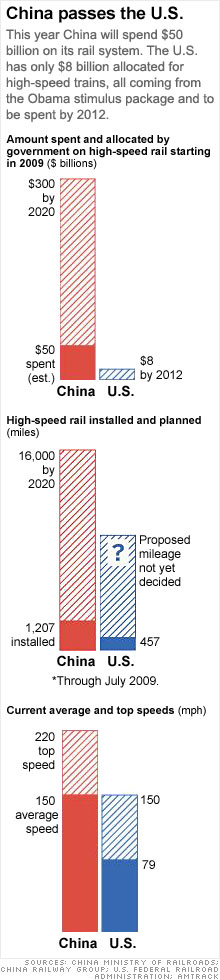
Image Courtesy:Fortune
It’s 95 degrees and humid — a typically oppressive summer day in southeastern China — but it’s not just mad dogs and Englishmen who go out in the midday sun.
Xi is among a vast army of workers in China — according to Beijing’s Railroad Ministry, 110,000 were laboring on a single line, the Beijing-Shanghai route, at the beginning of 2009 — who are building one of the largest infrastructure projects in history: a nationwide high-speed passenger rail network that, once completed, will be the largest, fastest, and most technologically sophisticated in the world.
Creating a rail system in a country of 1.3 billion people guarantees that the scale will be gargantuan. Almost 16,000 miles of new track will have been laid when the build-out is done in 2020. China will consume about 117 million tons of concrete just to construct the buttresses on which the tracks will be carried. The total amount of rolled steel on the Beijing-to-Shanghai line alone would be enough to construct 120 copies of the “Bird’s Nest” — the iconic Olympic stadium in Beijing.
The top speed on trains that will run from Beijing to Shanghai will approach 220 miles an hour. Last year passengers in China made 1.4 billion rail journeys, and Chinese railroad officials expect that in a nation whose major cities are already choked with traffic, the figure could easily double over the next decade.
Construction on the vast multibillion-dollar project commenced in 2005 and will run through 2020. This year China will invest $50 billion in its new high-speed passenger rail system, more than double the amount spent in 2008. By the time the project is completed, Beijing will have pumped $300 billion into it.
This effort is of more than passing historical interest. It can be seen properly as part and parcel of China’s economic rise as a developing nation modernizing at warp speed, catching up with the rich world and in some instances — like high-speed rail — leapfrogging it entirely.
Last November, as the developed world imploded — taking China’s massive export growth and the jobs it had created with it — Beijing announced a two-year, $585 billion stimulus package — about 13% of 2008 GDP.
Infrastructure spending was at its core. Beijing would pour even more money into bridges, ports, and railways in the hope that it could stimulate growth and — critically — absorb the excess labor that exporters, particularly in the Pearl River Delta, were shedding as their foreign sales shrank more than 20%.
At a moment when the developed world — the U.S., Europe, and Japan — is still stuck in the deepest recession since the early 1980s, China’s rebound is startling. And the news comes just as Washington is embroiled in its own debate about whether the U.S. requires — and can afford — another round of stimulus, since the first one, earlier this year, has thus far done little to halt the downturn. Tax cuts made up about one-third of the $787 billion package, and only $60 billion of the remaining $500 billion has been spent so far.
Proponents of more stimulus are likely to cite China’s example of what a properly designed stimulus program can accomplish. Maybe so. But a closer look at China’s high-speed rail program also reveals some risks that should factor into the “Why can’t we do that?” debate that’s surely coming in Washington.
Last year China Railway Construction Co., the nation’s largest railroad builder, hired 14,000 new university graduates — civil and electrical engineers mostly — from the class of 2008. This year, says Liang Yi, the vice CEO of the CRCC subsidiary working on the Beijing-to-Shanghai high-speed line, the company may hire up to 20,000 new university grads to cope with the company’s intensifying workload. But with the private sector cutting way back on hiring — and university students desperate for work — taking on that many new engineers and managers hasn’t been too difficult.
Consider that the Northeast Corridor, between Boston and Washington, D.C., is served by Amtrak’s Acela train, which clips along at a stately average speed of 79 miles an hour. There’s a lot of talk now, as part of President Obama’s stimulus plan, about upgrading the system and building new, faster lines all across the nation. In his stimulus bill Obama has allocated $8 billion over three years for high-speed rail, and 40 states are now bidding for the funds, with results to be released in September. Among the possibilities, California wants to link San Francisco with L.A. via a high-speed link. Senate Majority Leader Harry Reid (D-Nev.) wants the private sector to get into the act, proposing a high-speed spur to connect Las Vegas with L.A.
Click here to read the entire article.











![Image Courtesy: Economic Policy Institute [figure]](http://www.epi.org/page/-/img/20090805_snapshot.jpg)